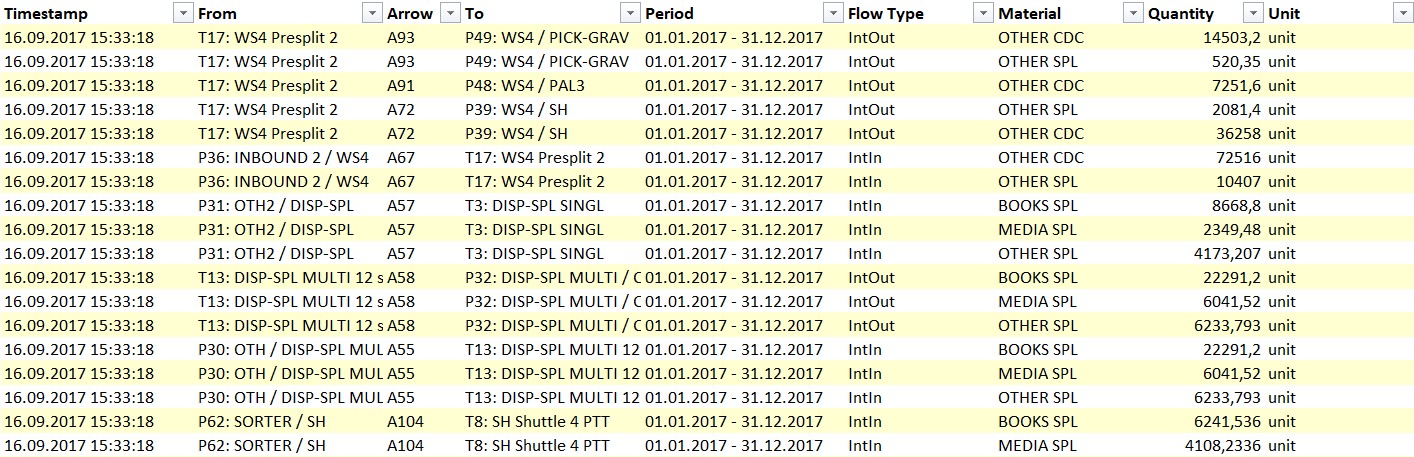
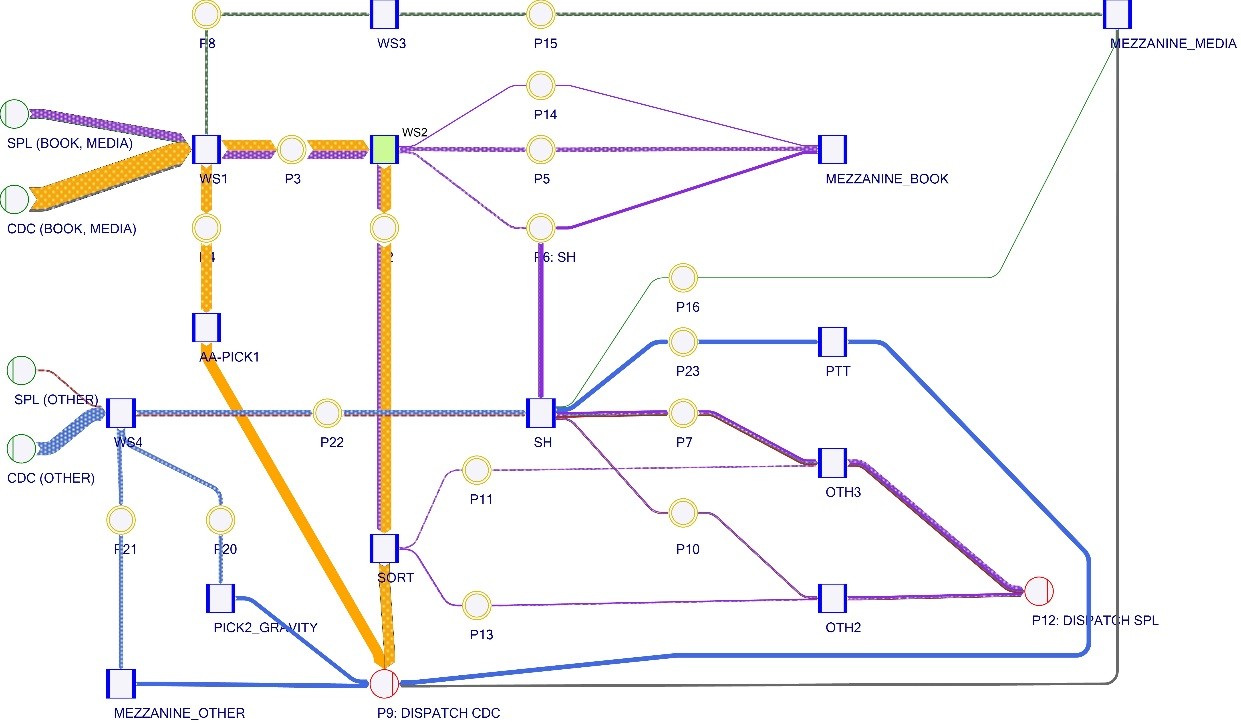
A computational method indicating the course, dependencies and results of the streams of incoming and outgoing units in a warehouse passing on their way through successive processes of preparation for dispatch. The results are usually expressed graphically by means of Sankey diagrams.
Keep readingStream analysis is used in logistics planning for individual commodity groups to determine the throughput of subsequent process nodes in the path of a given stream (e.g. preparation for picking, packing, etc.), which depends on the performance of the process node (e.g. human labour, equipment performance) and to determine the time in which a given stream can be processed at each quoted node.
The analytical method of stream analysis is ideal for modelling daily order profiles with a known number of staff or target number of items in a stream. It also makes it possible to determine the limit of a stream of goods that can be processed in a given warehouse with the existing or planned technical infrastructure.
A collection of machines and equipment, and the processes they carry out, combined in a single control platform that, thanks to its algorithms, makes it possible to operate a warehouse and carry out tasks involving the control of flows of goods. Warehouse automation has a positive impact on logistics processes, including: flow, storage and dispatch of goods by reducing the necessary resources.
Keep readingBenefits resulting from using automation in warehouses:
- reduction of the time of process execution
- increase in the warehouse’s performance
- increase in the accuracy of the executed work
- lowering warehousing costs
- increase in control over the warehouse inventory
- improvement of the flow of information
- better utilisation of the available human resources
- reduction of the number of errors (caused until now by the human factor)
What is worth noting when planning warehouse automation?
- identification of unprofitable flow areas
- Key Performance Indicators (KPI) analysis
- determination of the ROI (Return on Investment) in financial and time terms
- determination of the costs of machinery – both of its purchase and use
Detail Plan - detailed planning of the facilities and organisation of the warehouse and logistics flow in the warehouse. The Detail Plan mainly takes into account:
- determination of technical parameters of machinery and equipment
- degree of automation of warehouse systems
- physical properties of goods and any special transport conditions
Detail Plan - detailed planning of the facilities and organisation of the warehouse and logistics flow in the warehouse. The Detail Plan mainly takes into account:
- determination of technical parameters of machinery and equipment
- degree of automation of warehouse systems
- physical properties of goods and any special transport conditions
- goods flow stream analysis and optimisation
- infrastructure – surface capabilities of the lot, hall
- planned growth and opportunities for expanding the project
You will find more information on detailed planning here.
Also referred to as logistics consultancy, it is a set of services for optimising a company's current state of logistics and warehousing in relation to planned new investments in this area. It is based on taking a practical look at existing operations, finding key points and optimising them, and identifying opportunities for further development.
Keep readingLogistics consulting is key when an enterprise features the following:
- a logistics problem affecting other company departments and requiring a quick solution
- incorporation of a new investment requiring the development of new processes
- activities aimed at limiting costs
- employment restructuration
The following arguments speak for the participation of logistics consultants:
- process competence and experience: the fact of having carried out a large number of projects in many industries consolidates the related experience and provides a larger solution base - including an orientation to emerging technologies on the market, their possibilities and weaknesses in relation to the specific use case.
- good knowledge of the supplier market: the database of potential suppliers is disproportionately larger than that of the average logistics user, as well as knowledge of proven competence not based on directory information but verified in practice
- independence from the technology supplier: greater independence of consultants from the influence of the supplier, e.g. in sales discussions or when advertising the product, including specific conditions of use and actual performance achieved in practice
- a broad horizon of knowledge: in logistics process automation projects, it is necessary to know how the various technologies interact with each other so that they are complementary and not mutually exclusive - experience is required in the fields of automation, mechanics, IT, process and operational logistics, construction, fire safety, health and safety, statics, ergonomics, process analytics, goods streams and human behaviour when interacting with automation elements
- Competence for 3PL services: when building a logistics centre with the intention of offering logistics services to other industries, process knowledge is required for other product groups in addition to own products
- knowledge of the implementation and management of the project: during the implementation of the project, it is necessary to have competent supervision of the work of subcontractors and to know their techniques, including the standards governing and the criteria by which a system can be considered functionally correct and accessible to the user at the level implied by the standards or the commercial contracts concluded
- mediator: project implementation is almost certain to give rise to situations arising from differences in interest - this is where an objective view and the ability to find a position acceptable to all parties to the project come in handy
- having planning instruments: having a set of tools to carry out the process of flow analysis, conceptual planning, creation of tender documents, project management, supervision of vendor-independent start-up and resources
Graphical representation of operations and processes with their interrelationships. Describing the individual elements of the process map uses symbols and graphic icons linking all processes into process chains with their inputs and outputs.
Keep readingEach process mapping must include the following elements:
- process beginning and end
- process structure
- point of entry and exit to and from the process of its components
- definition of the actors taking part in the process (suppliers, employees, etc.)
- who is the process owner (in terms of using its result) or who is responsible for its supervision
- performance evaluation criteria (in practice, a maximum of 4 evaluation indicators are used, because an excessive number of them can cause mutual exclusion and process blockage in consequence)
- impact on the entire process chain – this can include, e.g. indicator of usefulness to develop the final result, the so-called success share indicator
- measurement tools
- criteria and tools for process control
- resources (human, assets, IT, etc.) intended for process execution and affecting its costs
- scenarios of deviation from the primary process
- process documentation
Conceptual planning - the first phase of real warehouse planning, following the logistics audit and data analysis. Conceptual planning takes into account the customer's infrastructure, the most important storage principles (analysis of consecutive processes, volumes of logistical flows) and the available technical solutions (racking, conveyors, automation).
Keep readingThe MASTER PLANNING process begins with the identification of the basic volumes of logistical flows from both the quantitative side and the structures that influence the choice of technology.
The results of statistical analyses (static from the point of view of the timeline for a process node) or dynamic analyses (determining point-to-point process flow rates) become the basis for analysing and mapping future processes.
As a result of pre-planning (high level1), an operational definition of the processes is created, i.e. a description of the assumed activities or the flow of goods. In the process definition, we also use methods to determine what parameters will be the variables and what effects (results of the process operation) we expect.
Building each master plan is based on the same principles, but ultimately there are no two identical master plans. Each of them is individually adapted to the following:
- company building
- infrastructure
- order specification
- devices and automation
- customer needs
1) Often encountered in practice an in talks with the customers expression based on the assumption that the initial planning process cannot include the consideration of process particulars with a depth typical for process algorithms
A quick audit of logistical processes, the task of which is to identify the current situation in the warehouse and make suggestions for optimising the processes taking place there.
Keep readingIt includes the collection of general data on the following topics:
- the product itself
- its distribution
- number of employees
- current state of automation
- current stream flow
- development opportunities and needs
- analysis of logistics processes and their performanc
A range of analytical and planning activities (e.g. Master Plan) aimed at planning the logistical process inside the warehouse in terms of three main factors:
- time
- costs
- quality
A logistics process includes, among others, the following:
- determination of analytical data
- stream analysis
- planning of processes to be implemented
- graphical design of the distribution of processes in space and time
- establishment of the investment budget, amount of required personal resources, return on investment
- functional analysis of processes
A flowchart is a graphical representation of a balance (e.g. of materials, energy). The graph consists of bands of an appropriate width, proportional to the quantity represented. What is important in a Sankey diagram is that the summed width of the input bands is equal to the summed width of the output bands. With stream diagrams, it is easy to identify where process losses occur (stream analysis).
Keep readingThe name of the diagrams is derived from the name of Matthew H. Sankey, an Irish engineer who was first to apply the aforementioned method to demonstrate energy losses during steam machine operation (1898).
Flow charts can be used to represent flows in systems of any scale. In the logistics and warehousing industry, they are used for the flow of warehouse processes, including goods and energy.
Example: